XB-IMG-145811
Xenbase Image ID: 145811
|
||||||||||
|
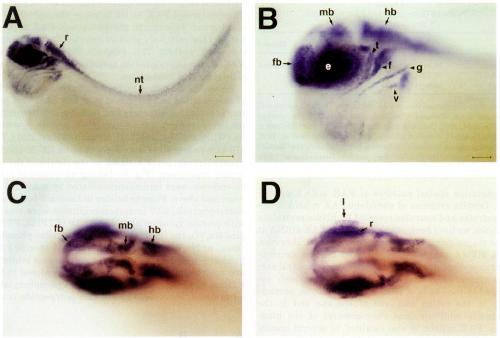
FIG. 4. Localization of Xenopus FAK mRNA by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Albino embryos were treated with digoxygenin-labeled
antisense RNA probes followed by incubation with an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-digoxygenin antibody. RNA hybrios were visualized
using the NBT/BCIP chromogenic reaction. (A) Side view of a stage 35 embryo. FAK expression is evident in structures of the central
nervous system in the head and trunk. Staining in the rhombomeres (r) is continuous with cellular staining in the neural tube (nt), which runs
along the length of the embryo. Faint staining is also evident in the caudal-most region of the somitic field of the trunk. (B) Higher magnification
of the head of the same embryo. FAK expression in cells of the forebrain (fb), midbrain (mb), and hindbrain (hb) and the eye {e) is indicated.
Positively stained cranial nerves are identified as trigeminal (t), facial (f), glossopharyngeal (g), and vagus (v). (C) Dorsal view of a similarly
staged embryo. Arrows indicate discrete localization of FAK mRNA in the lobes of the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. (D) Different focal
plane of the same embryo. FAK transcripts are localized to structures of the developing eye including the lens (I) and the developing retina (r).
Scale bars; A, 200 um; B-D, 100 um. Image published in: Hens MD and DeSimone DW (1995) Copyright © 1995. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
