XB-IMG-135121
Xenbase Image ID: 135121
|
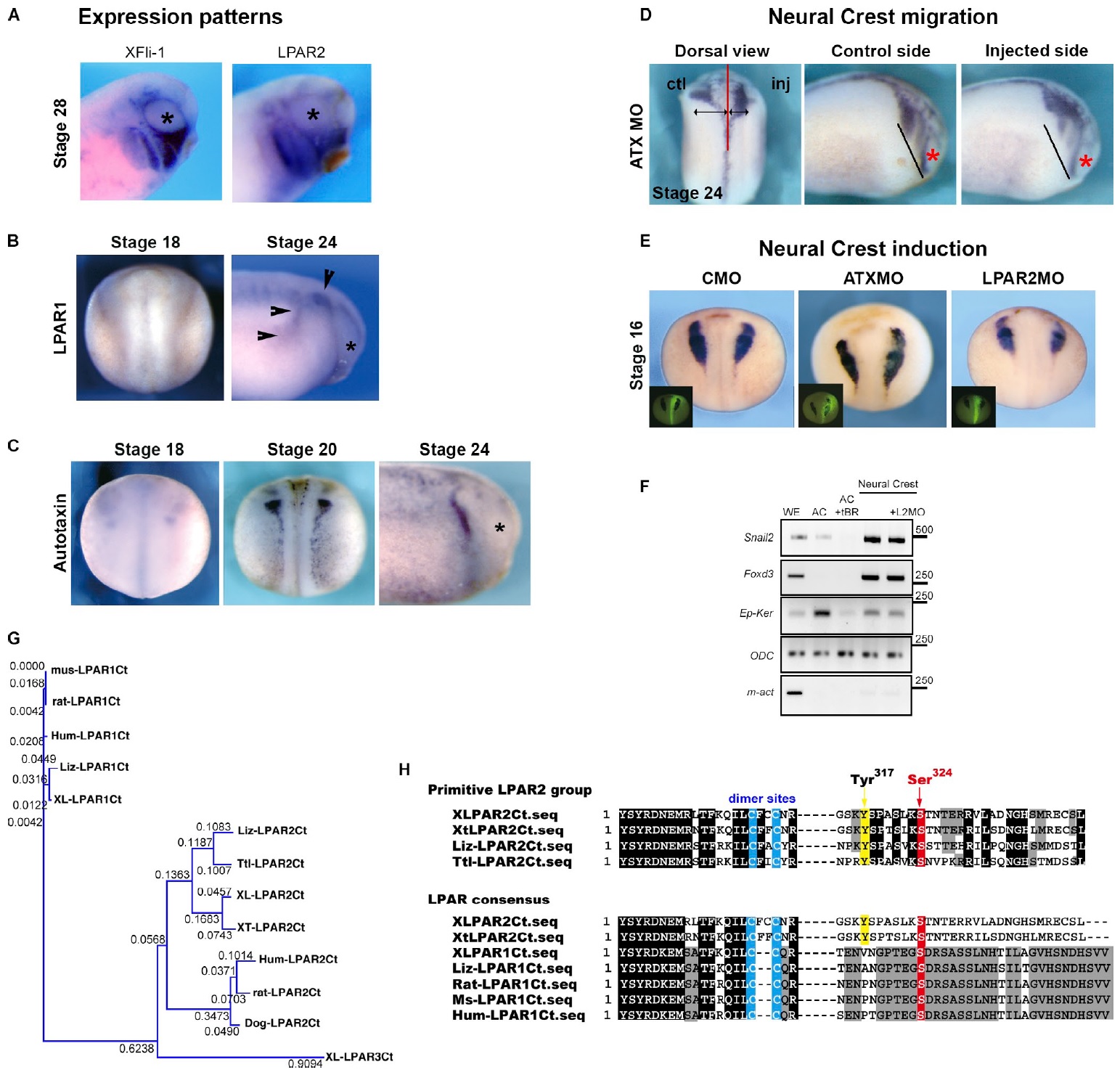
Figure S1. LPAR2 and Autotaxin are required for NC migration. (A) Lateral view of XFli1 (NC marker) and LPAR2 expression at postmigration stages.
(B) Expression of LPAR1 in premigratory (stage 18, dorsal view) and migratory stages (stage 24, lateral view). Arrowheads indicate the otic vesicle and an
ectodermal domain that appears to be expressing LPAR1. No expression was seen in NC cells. (C) Expression of Autotaxin at stage 18 and 20 (dorsal
views) and stage 24 (lateral view). ATX is first weakly expressed in the neural plate border region (St18) and is up-regulated in early migratory NC cells
(St20), and remains expressed in a subpopulation of migratory NC cells (St24). Asterisks indicate eyes. (D) Inhibition of ATX expression impairs NC migration
(St24, dorsal and lateral views). (E) Inhibitions of ATX or LPAR2 expressions do not affect NC induction (St18, Snail2 in situ hybridization; the inset
shows FDx on the injected side). (F) RT-PCR from RNA extracts obtained from whole embryos (WE), animal caps (AC), animal caps expressing truncated
BMP receptor (AC + tBR), or from NC cells obtained from animal caps coexpressing tBR and Wnt8, in the presence of LPAR2MO (L2MO). Snail2 and
Foxd3 are NC markers. Asterisks mark the eye. (G and H) Sequence analyses of LPAR2 and LPAR1. (G) Evolutional tree (NJ method; GENETYX) of LPAR’s
seventh cytoplasmic domain amino acid sequences (C-tail). LPAR2 sequences are categorized into two groups, relatively primitive animals (lizard, turtle,
frogs) and mammalian homologues (human, rat, mouse, dog), whereas the sequence homologies of LPAR1 are very high in C-tail among species. Right
panel, multiple sequence alignments of LPARs. Among the primitive species, Tyr317, Ser318, Ser321, and Ser324 are well-conserved. (H) We compared LPAR2
and LPAR1 sequences to generate a LPAR consensus sequence in which S324 is well conserved across species. Image published in: Kuriyama S et al. (2014) © 2014 Kuriyama et al. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
