Quantitative proteomics of Xenopus laevis embryos
Sun et al. published in Scientific Reports the expression kinetics of nearly 4000 proteins during early development of Xenopus laevis, the largest developmental proteomic dataset for any animal.
Analyzing embryos at NF stages 1, 8, 13, and 22, about 90% of ~5000 early transcribed genes are translated into protein. 4065 proteins were matched to gene symbols, 390 putative proteins have yet to be annotated. The proteins identified were separated into six clusters. Clusters 1 and 2 are proteins downregulated in the stage range analyzed. Clusters 3 and 5 are proteins encoded from maternal transcripts activated upon fertilization. Proteins in cluster 3 are upregulated, proteins in cluster 5 are upregulated by NF stage 8, but levels decrease as the embryos enter gastrulation. Proteins in cluster 6 represent those whose translation represent genes activated by zygotic transcription and protein expression going into the mid-blastula transition. Proteins in cluster 4 are those expressed as the embryos transition from gastrulation into neurulation, between NF stages 13 and 22. The identified proteins are also characterized by biological process information within these clusters. The cluster profiles mark changes in gene expression patterns at key events in early Xenopus laevis development.
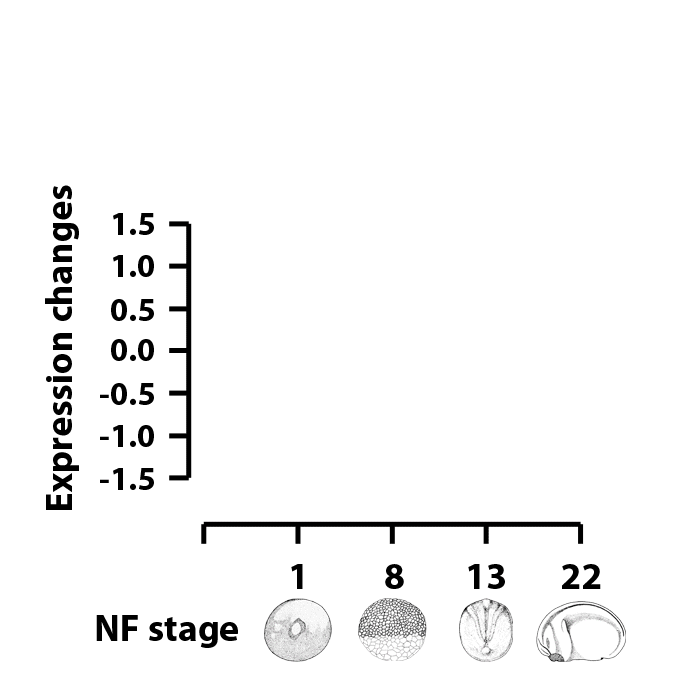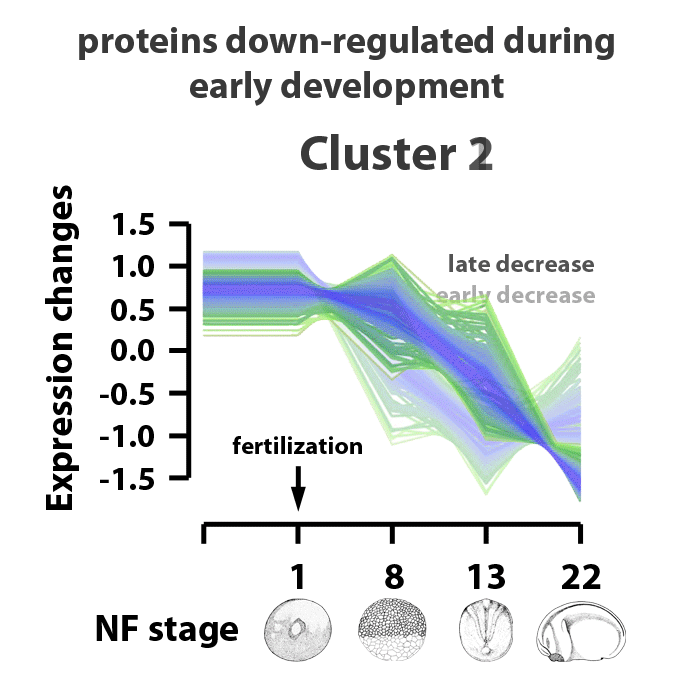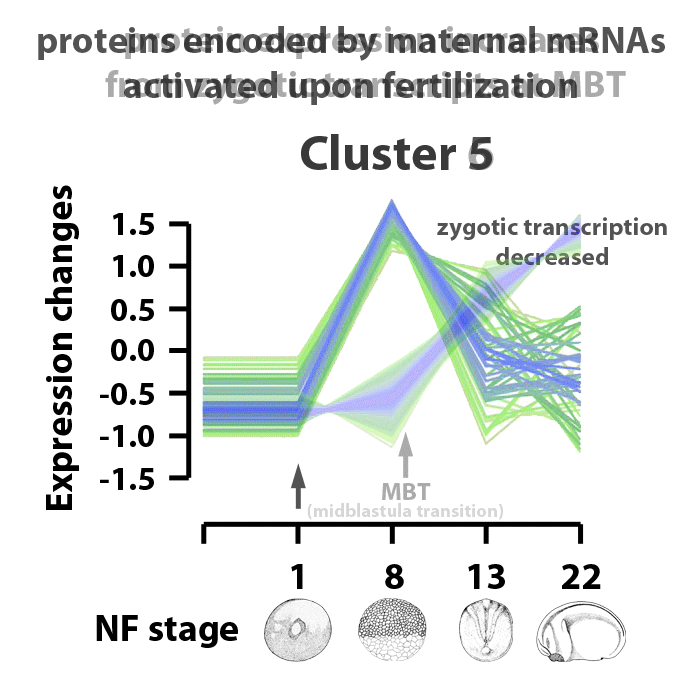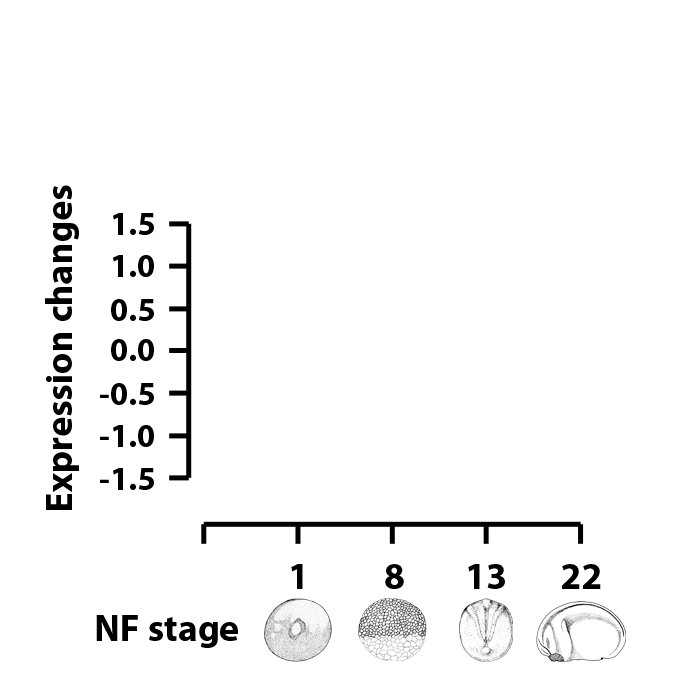
Image adapted from figure 2 of Sun et al., Scientific Reports 4, Article number: 4365 doi:10.1038/srep04365
Click here for Paul W. Huber's Xenbase page.
Click here for Norman J. Dovichi's Xenbase page.
Images created by VGP, copyright Xenbase.
Last Updated: 2014-04-24